Thief’s Bite Almost Costs Store Owner His Arm
A store owner nearly lost his arm after being bitten by a thief during a robbery attempt that turned into a life-threatening medical emergency.
The 60-year-old shop owner in Istanbul, Turkey, learned firsthand that a human bite can be far more dangerous than a dog bite. What began as a crime in 2024 later became a remarkable medical case, documented by Turkish doctors in a medical journal and reported by t4newsmedia.com on September 16, 2025.
The incident happened in Üsküdar, a busy residential district on the Asian side of Istanbul. As the store owner was closing his shop, two masked men broke in and attempted to rob him. Refusing to give in, he fought back and managed to grab one of the thieves. In a desperate attempt to escape, the thief bit the store owner’s left hand with such force that he was forced to let go. Both suspects then fled, leaving the store owner injured.
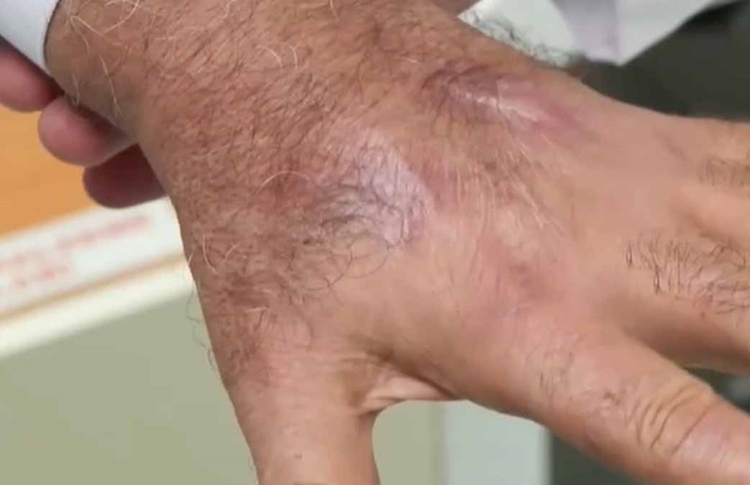
He received initial treatment at a local clinic and was sent home. However, within a few days, his condition worsened dramatically. He developed a high fever, severe chills, and intense swelling in his left hand. By the time he was admitted to Sultan Abdulhamid Han Training and Research Hospital, his hand had nearly doubled in size and started to change color — clear signs of a serious infection.
Doctors treated him with antibiotics for two weeks, but his condition did not improve. Fearing the infection would spread and threaten his life, they considered amputating his hand. As a last resort, they turned to hyperbaric oxygen therapy, a procedure that pushes oxygen deep into infected tissue to kill bacteria and speed up healing.

Thankfully, the therapy worked. The swelling gradually subsided, allowing doctors to remove the dead tissue and save his hand. After months of physiotherapy, the store owner was able to regain full use of his hand.
According to Dr. Yavuz Aslan, one of the attending physicians, bacteria from a human mouth can penetrate deep into tissue and cause severe infections that are difficult to treat, even with strong antibiotics.
